Ministério da Economia (Ministry of Economy)
ICP- Autoridade Nacional de Comunicações (ICP ? National Communications Authority)
Notice
Radioelectric licenses
In compliance with no. 2 of article 8, with no. 2 of article 9, with no. 3 of article 12 and with no. 2 of article 18, all of them part of the Decree-Law no. 151-A/2000, of 20 July, it is hereby made public, by determination of the Board of Directors of ICP-Autoridade Nacional de Comunicações, of 10 July 2003, that the Notice published in Diário da República ( Government’s Official Gazette), 3rd series, no. 40, of 14 February 2003 is replaced, and the following shall apply regarding radioelectric licenses:
Stations needing licenses
1 Pursuant to paragraph no. 2 of article 8, the following radiocommunication stations need licenses:
1.1 In the Fixed Service:
The Fixed Stations of Short Wave connections (FS/SWC) 1;
1.2 In the Satellite Fixed Service:
1.2.1 The Earth Stations (FSS/ES) 2 , excluding VSAT stations operating in frequency bands exclusively attributed for that effect;
1.2.2 The Earth Stations for “Satellite News Gathering” (FSS/SNG) 3.
1.3 In the Mobile Air Communications (MAC) 4: Air Communication Stations.
1.4 In the Mobile Sea Communications (MSC) 5: The Coastal Stations and the Harbour Stations.
1.5 In the Broadcasting Service: the Analogical Television (BS/ATV) 6 Broadcasting and/or retransmitters stations, the Analogical Sound Broadcasting(BS/ASB) 7 and the Sound Broadcasting of the “Digital Radio Mondiale” system (BS/DRM) 8.
1.6 In the Radiodetermination Service: The Radiodetermination Stations (RDTS) 9.
Exemption of network licence
2. Pursuant to paragraph a) of no. 1 and no. 2 of the article 9, are exempt from licensing:
2.1 The networks in which are included all the stations referred to in no. 1;
2.2 The following radiocommunication networks:
2.2.1 Privative Networks of the LMS for Private Radio Paging (CSPP), with the following characteristics:
|
Characterization of the stations |
|||
|
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power range |
Antenna Type |
Carrier frequency spacing |
|
40,680 MHz |
5 W e.r.p. |
external – Base station Integrated - portable |
20 kHz |
|
169,175 MHz |
5 W e.r.p. |
external - Base station Integrated - portable |
25 kHz |
|
468,1125 MHz |
2 W e.r.p. |
external - Base station Integrated - portable |
12,5 kHz |
|
468,1250 MHz |
2 W e.r.p. |
external - Base station Integrated - portable |
|
|
469,275 MHz |
5 W e.r.p. |
external - Base station Integrated - portable |
25 kHz |
2.2.2 Wireless telephones (CTs), with the following characteristics:
|
Characterization of the stations |
||||
|
System Technology |
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power range |
Antenna Type |
Carrier frequency spacing |
|
CT0 (analogical) |
27,5375 - 27,8375 MHz |
Transmitter output power: 10 mW
|
Integrated or dedicated
|
25 KHz
|
|
36,9875 - 37,2875 MHz |
||||
|
CT1 (analogical) 1https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55129 |
914-915 MHz |
Integrated |
25 KHz |
|
|
959-960 MHz |
|
|||
|
DECT(digital) |
1880-1900 |
Transmitter output power: 250 mW |
Integrated or dedicated |
1,728 MHz |
Exemption of station licence
3 Pursuant to paragraph b) of no. 1 and no. 2 of the article 9, are exempt from licensing:
3.1 The Station with low power and short range (“SRD-Short Range Devices”)
These stations should operate in a non interference and non protection basis relatively to
licensed radiocommunication stations and networks
|
Characterization of the stations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Usage |
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power range or field strength |
Antenna Type
|
Carrier frequency spacing |
“Duty Cycle” |
|
General Usage 2https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55130
|
6,765 - 6,795 MHz |
42 dBμA/m a 10 m |
Integrated or dedicated
|
Occupation of the whole band |
|
|
13,553 - 13,567 MHz |
|||||
|
26,957 - 27,283 MHz |
|||||
|
26,957 - 27,283 MHz |
10 mW e.r.p. |
||||
|
40,660 - 40,700 MHz |
|||||
|
433,050 - 434,790 MHz 3https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55131, 4
|
< 10% |
||||
|
868,000 - 868,600 MHz |
25 mW e.r.p. |
< 1% |
|||
|
868,700 - 869,200 MHz |
< 0,1% |
||||
|
869,400 - 869,650 MHz |
500 mW e.r.p. |
25KHz 9https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55138 |
< 10% |
||
|
869,700 - 869,870,000 MHz |
5 mW e.r.p. |
Occupation of the whole band
|
Up to 100% |
||
|
2400 -2483,5 MHz |
10 mW e.i.r.p. |
|
|||
|
5725 - 5875 MHz |
25 mW e.i.r.p. |
||||
|
24,00 - 24,25 GHz |
100 mW e.i.r.p. |
||||
|
61,00 - 61,50 GHz |
|||||
|
122 - 123 GHz |
|||||
|
244 - 246 GHz |
|||||
|
Radio Local Area Network (RLANs) |
2400-2483,5 MHz |
100 mW e.i.r.p.5https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55133 |
Integrated or dedicated |
Occupation of the whole band binary rhythm» 250 kbps |
|
|
High Performance Radio Local Network (HIPERLANs) |
5150-5350 MHz,6https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55134 7
|
200 mW e.i.r.p.8https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55137 |
dedicated |
Occupation of the whole band |
|
|
5470-5725 MHz6https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55134 |
1 mW e.i.r.p.8https://www.anacom.pt/render.jsp?contentId=55137 |
||||
|
17,1-17,3 GHz |
100 mW e.i.r.p. |
||||
|
Railways-Eurobalise |
27,095 MHz |
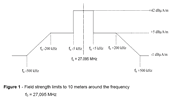
See pictures 1 |
|
See pictures1 |
|
|
Telemetry Sistems for Road Transportation- Toll system |
5797,5 MHz +/- 2,5 MHz |
2 mW e.i.r.p. |
Integrated or dedicated |
5 MHz |
|
|
5800 MHz +/- 5 MHz |
10 MHz |
||||
|
5802,5 MHz +/- 2,5 MHz |
5 MHz |
|
Usage |
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power range or field strength |
Antenna Type |
Carrier frequency spacing |
Duty Cycle |
|
Detection of movement and alert |
2400 - 2483,5 MHz
|
25 25 mW e.i.r.p. |
Integrated or dedicated |
Occupation of the whole band |
|
|
9200 - 9500 MHz
|
|||||
|
9500 - 9975 MHz
|
|||||
|
13,4 - 14,0 GHz |
|||||
|
24,05 - 24,25 GHz |
100 mW e.i.r.p. |
||||
|
Alarms in general |
868,600 - 868,700 MHz |
10mW e.r.p |
Integrated or dedicated |
25 KHz |
< 0 ,1% |
|
869,250 - 869,300 MHz |
25mW e.r.p |
||||
|
869,650 - 869,700 MHz |
< 10% |
||||
|
Social Alarms |
869,200 - 869,250 MHz |
10mW e.r.p |
< 0 ,1% |
||
|
Model Control
|
26,995 MHz |
100mW e.r.p |
dedicated
|
10 KHz
|
|
|
27,045 MHz |
|||||
|
27,095 MHz |
|||||
|
27,145 MHz |
|||||
|
27,195 MHz |
|||||
|
34,995 - 35,225 MHz 10 |
|||||
|
40,665 MHz |
|||||
|
40,675 MHz |
|||||
|
40,685 MHz |
|||||
|
Inductive Systems |
9 - 59,750 kHz |
72 dBμA/m at 10 m (a |
Integrated dedicated or external |
Occupation of the whole band
|
|
|
59,750 - 60,250 kHz |
42 dBμA/m at 10 m |
||||
|
60,250 - 70 kHz |
72 dBμA/m at 10 m (a |
||||
|
70 - 119 kHz |
42 dBμA/m at 10 m |
||||
|
119 - 135 kHz |
72 dBμA/m at 10 m (a |
||||
|
6,765 - 6,795 MHz |
See picture 2 |
Integrated or dedicated |
|||
|
7,400 – 8,800 MHz |
9 dBμA/m at 10 m |
||||
|
13,553 - 13,567 MHz |
See picture 2 |
||||
|
26,957 - 27,283 MHz |
42 dBμA/m at 10 m |
||||
|
Active medical implantations |
402 - 405 MHz | 25μW e.r.p. | 25 KHz | ||
| 9 - 135 kHz | 30dBμA/m at 10 m |
Occupation of the whole band |
< 10% | ||
|
Wireless Audio systems |
863 - 865 MHz | 10 mW e.r.p. | Integrated | 300 KHz | Up to 100% |
| 864,8 - 865 MHz | 50 KHz | ||||
|
Emitting Microphones |
863 - 865 MHz | 10 mW e.r.p. | Integrated | 200 KHz |
|
Usage |
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power |
Antenna Type |
Carrier |
Duty Cycle |
|
Remote control, telemetry,
|
29,980 MHz |
100 mW e.r.p. |
|
10 kHz |
|
|
29,990 MHz |
|||||
|
30,000 MHz |
|||||
|
30,100 MHz |
|||||
|
150,9375 MHz |
500 mW e.r.p. |
12,5 kHz |
|||
|
150,9500 MHz |
|||||
|
155,5375 MHz |
|||||
|
155,5500 MHz |
|||||
|
458,1125 MHz |
|||||
|
458,1250 MHz |
|||||
|
458,1375 MHz |
|||||
|
458,1500 MHz |
3.2 Transportable earth stations of the Satellite Fixed Service (FSS).
These stations should operate in a non interference and non protection basis relatively to licensed radiocommunication stations and networks
The utilization of this kind of earth stations are only allowed for distances greater than 500 meters from the airports limit area.
The utilization of the earth stations with permanent fixed location is not covered by this exemption regime.
|
Characterization of the stations |
|||
|
Earth Station |
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power |
Antenna Type |
|
“Satellite Interactive Terminal (SIT)” |
10,70 - 12,75 GHz (space-Earth) |
Broadcasting power < 2 W |
Antenna with diameter < 1,2m |
|
“Satellite User Terminal (SUT)” |
19,70 - 20,20 GHz (space-Earth) |
|
|
|
“Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT)” |
12,50 - 12,75 GHz (space-Earth) |
Antenna with diameter < 3,8 m |
|
|
“Arcanet Suitcase Terminal” |
11,45 - 11,70 GHz (space-Earth) |
|
|
3.3 The Earth Stations of the Satellite Mobile Services.
|
Characterization of the station |
|
|
Earth Station |
Frequency Bands |
|
Inmarsat-B |
1525 - 1544 MHz (space-Earth) 12 |
|
Inmarsat-C |
|
|
|
|
|
Inmarsat-M |
|
|
Inmarsat-M4 |
|
|
Inmarsat-phone (mini M) |
|
|
EMS-PRODAT |
|
|
EMS-MSSAT |
|
|
Thuraya |
|
|
SpaceCheckers-SMS |
|
|
Omnitracs-Eutelsat |
10,70 - 11,70 GHz (space-Earth) 15 |
|
|
1610 – 1626,5 MHz (Earth -space) |
|
Mobile Earth Stations (MES) |
137 – 138 MHz (space-Earth) |
3.4 The Land Mobile Service stations
Station Land Mobile Service station
|
Characterization of the stations |
|
|
|
|
Frequency Bands |
Maximum power |
Antenna Type |
Carrier frequency |
|
446,00625 MHz |
500 mW e.r.p. |
Integrated |
12,5 kHz |
|
|
|||
|
446,03125 MHz |
|||
|
446,04375 MHz |
|||
|
446,05625 MHz |
|||
|
446,06875 MHz |
|||
|
446,08125 MHz |
|||
|
446,09375 MHz |
3.5 The radiocommunication stations of plain reception.
|
Characterization of the stations |
|
Includes the following receiver stations:
|
FIGURES :
Eurobalise
Figure 1 - Field strength limits to 10 meters around the frequency
f0 = 27,095 MHz
Inductive Systems
Figure 2 - Field strength limits to 10 meters for the frequency bands
6,765 - 6,795 MHz and 13,553 - 13,567 MHz
9
Mobile Land Stations GMPCS
Figure 4 – Marking placed on the stations GMPCS
DEFINITIONS:
“SRD-Short Range Devices” - The designation “Sort Range Devices” (SRDs, Short Range Devices) is meant to include the radio transmitters which establish uni-directional or bidirectional communications and those unlikely of causing interferences to other radio equipment. The SRDs uses integrated, dedicated or external antennas, being allowed all types of modulation as long as they fulfil whatever is specified in the relevant norms. Given the diversity of supplied services of this equipment, no description can be exhaustive enough.
Applications for railways - Specific applications for railways, including automatic vehicle identification and balises (Train control system)
Telemetry systems for road transportation - Communication systems for transportation support (mobile data links amongst vehicles and between vehicles and the infrastructure)
Movement detection and alert - Movement detection equipment and alert equipment (low power radar systems for the purpose of radiodetermination: determination of position, of speed and/or other characteristics of an object, or then obtaining information relative to these parameters).
Model Control – Movement control equipment for models in the air, on land and above or under the water.
Inductive Systems – Vehicle immobilizer, animal identification, alarm systems, cable detection, surplus management, personnel identification, voice wireless links, access control, proximity sensors, theft prevention systems including RF systems of theft prevention induction, data transfer for portable equipment, goods automatic identification, wireless control systems and automatic toll systems.
Active medical implantation with very low power - Instruments, apparatus, devices, materials or other goods, to be used isolated or jointly, for: diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or mitigation of illness; diagnosis, monitoring, treatment or mitigation or compensation of injury or deficiency; examination, substitution or modification of anatomy or of a physiological process; conception control.
Wireless audio systems – Wireless loudspeakers; wireless headphones; wireless headphones for portable use, for example CD and cassettes players or portable radios; wireless headphones for use inside vehicles, for example for use in radios, telephones, etc.; auricular monitoring for use in concerts or other type of stage productions.
Effective radiated power (ERP) in a given direction - the product of the power supplied to the antenna by its gain relative to a half-wave dipole in a given direction.
Equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) in a given direction - the product of the power supplied to the antenna by its gain relative to an isotropic antenna in a given direction (absolute or isotropic gain)
Average equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) – it is equal to the average of EIRP throughout a data burst, whenever the power control is at its maximum.
Integrated antenna – non removable antenna
Dedicated antenna – removable antenna supplied with the station
External Antenna – antenna not suitably designed for certain type of station
Spread Spectrum - the transmission technique where the signal occupies a bandwidth much larger than the minimum necessary to send information;
Frequency hopping spread spectrum - the technique of spread spectrum where the information is sent over several channels in a pseudo-aleatory form;
Direct sequence spread spectrum - the technique of spread spectrum where the information is combined with a pseudo-aleatory code;
“Duty cycle” – It is a relation, expressed in percentage, of the maximum period of time where equipment is active with one or more carriers, relatively to one hour period.
Interference - the effect caused on the reception, in a radiocommunication system, by an unwanted energy due to some emission, radiation or induction (or a combination of these emissions, radiations or inductions) and that is clearly shown by the degradation of the transmission quality, by the deformation or loss of information that could be obtained in the
absence of that unwanted energy.
Elements that must instruct the applications for the attribution of radioelectric licenses and requisites for technical projects to be presented
4 In compliance with provisions of paragraph 3 of article 12, the elements that must instruct the applications for the attribution of radioelectric licenses, as well as the requisites of technical projects to be presented by radioelectric license type and for
each service, are the following ones:
4.1 Network License
4.1.1 Elements to be presented for the licensing of private networks of the Land Mobile
Service (LMS/RPR)10:
Application indicating the bands for localized networks.
- Applicant’s identification;
- Correspondence addresses;
- Network objective;
- Network structure;
- Location of the stations;
- Service area;
- Number of stations;
- Number of requested channels;
- Applicant’s signature.
Application for licensing of localized networks
- Applicant’s identification;
- Collecting Address;
- Project;
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
Application for licensing of networks without fixed structures
- Applicant’s identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Preferred frequency bands;
- Number and justification for the requested channels;
- Number of stations;
- Service area;
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
Requisites for Technical Projects – localized networks
- Identification elements;
- Network generic characteristics;
- Class and location of the stations;
- Bands and working method;
- Installation diagram of the stations;
- Calculations of E.R.P.;
- Network devices;
- Identification of the project manager;
4.1.2 Elements to be provided for licensing of the Fixed Service networks – Point to
Point Link (FS/PPL)11, Studio -Transmitter Link (FS/STL)12.
Application:
- Applicant’s identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Network objective;
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
Requisites of the technical project:
- Identification Elements;
- Diagram of the requested links;
- Location of the stations;
- Links characteristics;
- Characteristics of the antenna systems;
- Link calculations;
- Identification of the project manager;
4.1.3 Elements to be provided for licensing of Broadcasting Service networks
(BS/DVB-T13 and BS/T-DAB14).
Application:
- Applicant’s identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Network identification;
- Location of the stations;
- Characteristics of the station antenna systems;
- Calculation of the stations E.R.P.;
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature;
4.1.4 Elements to be provided for licensing of other services networks.
- Fixed Service – Transportable Links (FS/FT)15, Electronic News Gathering,
(FS/ENG)16, Point-Multipoint Link (FS/PML)17;
- Satellite Fixed Service – Earth Stations (SFS/VSAT)18;
- Land Mobile Service – Public Networks (LMS/GSM19, LMS /UMTS20,
LMS /RPA21, LMS /TETRA22, LMS /CP23).
Application
- Applicant’s Identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Network objective (not applicable to Land Mobile Service – Public Networks)
- Location of the stations;
- Estimated maximum power (applicable to Land Mobile Service – Public Networks);
- Link characteristics;
- Characteristics of the antenna systems;
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
4.2 Station License
4.2.1 Elements to be provided for licensing of the stations requiring presentation of technical project.
- Fixed Service – Short Wave (SF/SW) 1
- Broadcasting Service - Analogical Sound (BS/BAS)7
Application
- Applicant’s Identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Network/Station objective;
- Attested copy of the certificate allowing the exercise of the activity ( applicable to
analogical sound broadcasting)
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
Requisites of the Technical Project (FS/SW) 1
- Identification Elements;
- Diagram of requested links;
- Location of the Stations;
- Link characteristics;
- Characteristics of the antenna systems;
- Link calculations;
- Identification of the project manager.
Requisites of the Technical Project (BS/BAS) 7
- Elements of Identification, including the studios location, the link method to the
station (applicable in the scope of local stations) and the location of the station.
- Technical characteristics of radiocommunication equipment to be used;
- Exact location (geographical co-ordinates) of broadcast antenna, location quota
and height of the antenna support tower;
- Power Calculations;
- Reasoned outline of the installation, based in measurements of field intensity, for
the cases pursuant to article 2 of the Decree-Law no. 126/2002, 10 May;
- Identification of the project manager.
4.2.2 Elements to be provided for licensing of the stations which does not require the
presentation of the technical project:
- Satellite Fixed Service – Land Stations (SFS/LS2 e SFS/SNG3);
- Mobile Air Communications (MAC) 4;
- Mobile Sea Communications (MSC) 5;
- Broadcasting Service – Analogical Television (BS/ATV)6
- Broadcasting Service - “Digital Radio Mondiale” (BS/DRM)8
- Radiodetermination Service (SRDT)9.
Application
- Applicant’s identification;
- Correspondence and collecting addresses;
- Network/station objective;
- Location of stations;
- Characteristics of the antenna systems;
- Power calculations (applicable to Analogical Television stations and
radiodetermination);
- Link characteristics (applicable to Land Stations);
- Applicant’s lawful witnessed signature.
4.2.3 The application forms for licensing of stations and radiocommunication services network, when available, can be obtained at ICP - Autoridade Nacional de Comunicações’ Head-Office and Delegations.
Lisbon, 10 July 2003
The Chairman of the Board of Directors
1 In compliance with the Decision ECC/DEC/(01)01, adopted by the Portuguese Administration, these frequency bands are no longer identified for this type of equipment; meanwhile the necessary measures will be taken allowing gradually the reduction of its utilization, with the objective of freeing the frequency bands until end of 2008.
2 Video Applications are only allowed above 2,4 GHz
3 In this band, applications of audio and voice signals, are not allowed
4 In the 433, 05 - 434,790 MHz band are also allowed the utilizations with 100% of ducty cycle limited to 1 mW de e.r.p.In the 434, 04 - 434,790 MHz sub-band is allowed utilizations with 100% of ducty cycle limited to 10 mW de e.r.p.
5 For systems using techniques of spectral scattering by direct sequence, the value of the spectral density of maximum power must be limited to -20 dBW/1 MHz; for systems using techniques of spectral scattering by frequency jump, the value of the spectral density of maximum power must be limited to -10 dBW/100 kHz.
6 The following conditions, should be observed : 1) In the 5150 - 5350 MHz band are only allowed utilizations “indoor” 2) Control of transmitted power to guarantee a factor of attenuation of at least 3 dB; 3) Dynamic selection of frequencies associated with the channel selection mechanism in such a way to allow a uniform scattering of a minimum of 330 MHz in the 5150 - 5350 MHz bands and of 255 MHz in the 5470 - 5725 MHz bands.
As intermediate solution and for a limited period of time, applications without dynamic selection of limited frequencies are allowed to the frequency bands of 5150 - 5250 MHz, with a maximum power limit of 60 mW of e.i.r.p. for applications with automatic power control and a maximum power limit of 30 mW of e.i.r.p. for applications without automatic power control. This situation will be revaluated opportunely.
Maximum value of average e.i.r.p.